How Is the Wavelength of a Longitudinal Wave Determined
The frequency is 066 Hz 6 crestssec 91 s. If a standing wave exists in a length of L then the number of waves that t into the length determine the wavelength.

Sound The Science Of Waves How They Travel How We Use Them Physics Lessons Ultrasound Physics Teaching Science
C is the speed of the wave.

. Relationship of wavelength and frequency. The wavelength in a longitudinal wave refers to the distance between two consecutive compressions or between two consecutive rarefactions. Longitudinal waves compressional wave the vibration of the individual particles is parallel to the direction of wave propagation ex.
Whereas a rarefaction is a region of low pressure on a wave and it can be related to the trough of a transverse wave. The musical note A is a sound wave. Therefore you can input data for any two of the three components and in different measurement units in order to discover the third value.
Determine the frequency of a microwave 60 cm in length. You can find it the same way you would for most other waves with the formula of vf. What is the wavelength of a sound wave with a frequency of 50 Hz.
It can be determined by estimating the horizontal distance between any two interconnected points on the wave whether longitudinal or transverse. To summarise we have that v lambda cdot f where. All of the frequencies or.
The speed of the wave is 066 24m 158 ms. The wavelength can always be determined by measuring the distance between any two corresponding points on adjacent waves. By measuring between adjacent rarefactions.
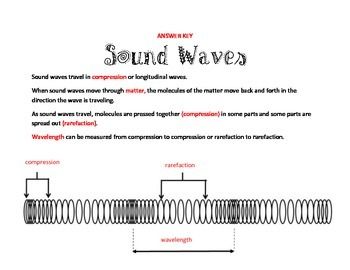
In the case of a longitudinal wave a wavelength measurement is made by measuring the distance from a compression to the next compression or from a rarefaction to the next rarefaction. A microwave is an electromagnetic wave. A compression is a region of high pressure on a wave and it can be related to the crest of a transverse wave.
Every wave has its own wavelength and you can easily determine the frequency and. The wavelength can always be determined by measuring the distance between any two corresponding points on adjacent waves. The amplitude of a wave is the height of a wave as measured from the highest point on the wave peak or crest to the lowest point on the wave trough.
Speed of longitudinal waves. In the case of a longitudinal wave a wavelength measurement is made by measuring the distance from a compression to the next compression or from a rarefaction to the next rarefaction. Longitudinal wave pulses will travel away from the point of release in both directions along the slinky.
The wavelength is actually the distance between two consecutive crests and troughs. We call this equation the wave equation. In the case of a longitudinal wave a wavelength measurement is made by measuring the distance from a compression to the next compression or from a rarefaction to the next rarefaction.
The wavelength is the measure of the waves extent. Longitudinal waves in a variable length air column. Frequency refers to the number of waves that pass a given point in a given time period and is often expressed in terms of hertz Hz or cycles per second.
Reviewing the sine function previously given the wavelength of the longitudinal wave is embedded in the wave number k. Wavelength is 12m Velocity frequency x wavelength 1000x035 350ms 30 degrees Celsius 346ms. T is the time elapsed.
You can also use the wavelength calculator to find out the frequency of a wave as long as you know its speed and wavelength. For a longitudinal wave the rarefactions and compressions are equal to crests and troughs for transverse waves. The wavelength in a longitudinal wave is the distance between two consecutive points that are in phase.
The frequency of a light wave. The wavelength is 24 m the distance between crests. It travels through space at a speed of 30 x 10 8 ms.
On the diagram above the distance from point A to point C or from point B to point D would be representative of the wavelength. Waves in which the medium moves back and. Velocity frequency x.
The part of a longitudinal wave where the particles of the medium are close together. Speed of sound is 342 ms. A wave transmits the energy from one position to another without fixed displacement of the particles of the medium where it propagates.
Sound or pushing the slinky forward condensations. Y x t y 0 c o s ω t x c Where y is the displacement of the point on the traveling sound wave. How is the wavelength of a longitudinal wave determined.
The answer from the tool will be given in the SI measurement unit for that variable. So the distance between one compression to the next or from rarefaction. Wave is the wave propagation speed is the wavelength.
The distance between two adjacent similar points of a wave. Determines amount of energy. Y 0 is the amplitude of the oscillations.
Longitudinal waves have compressions and rarefactions. V speed in textms-1 lambda wavelength in textm f frequency in textHz temp text. How is wave length determined for a longitudinal wave.
X is the distance the point traveled from the waves source. Relationship of amplitude and energy. Lnumber of complete sine waves Note that the number of complete sine waves may be fractional.
By measuring the wavelength of a wave you can measure the energy of the wave. It is equivalent to eqkfrac 2pi. Pick a point on the slinky about 13 the distance from one end at 𝑥 𝐿3 pinch a group of coils together at that point start data collection and quickly release the.

Understanding Tesla S Inventions Page 1 Longitudinal Wave Ultrasound Physics Physics And Mathematics

Longitudinal Vs Transverse Waves Physics Experiments Life Hacks For School 6th Grade Science
Sound Longitudinal Wave Notes Longitudinal Wave Waves Compression Wave
Comments
Post a Comment